Case Sharing │ Autologous CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Extramedullary Relapse of B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Case Introduction
The child, female, 7 years old, was admitted to our hospital due to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (medium risk, CR1) and central nervous system leukemia, medium-risk chemotherapy in CCLG-15 regimen for 1 year and right lower jaw enlargement for 1 month.
Diagnosis Process
First visit to Our Hospital on May 21, 2018
In April 2018, the child developed progressive right lower jaw enlargement for no obvious reason, up to about 8cm × 5cm × 4cm, with tenderness and high skin temperature, but no fever, dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting. In a local hospital, the child had poor response to anti-infective treatment, and no abnormalities were found in the bone marrow and cerebrospinal fluid in repeated examinations. On May 15, 2018, the right lower jaw mass puncture was performed in another hospital, pathological biopsy: meeting the diagnostic criteria for lymphoma in morphology, immunohistochemistry: MPO (few local lesions +), CD20 (scattered +), PAX-5 (diffuse +), TdT+, Ki-67 (about 90% +), CD7-, CD3-, meeting the diagnostic criteria for "B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma". On May 21, 2018, the child was admitted to our hospital for further diagnosis and treatment.
PET-CT after admission: multiple soft tissues and masses on the right neck, under the jaw and on the clavicle, increased glucose metabolism, (SUV1.2/1.7) meeting the manifestations of B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia; right mandibular ramus bone involved and damaged; diffuse uneven increase of bone marrow glucose metabolism in the whole body, and soft tissue shadows in some medullary cavities, meeting the manifestations of extensive bone infiltration of tumor.
History of Primary Disease on Admission
Blood Routine Test for Primary Disease: White Blood Cell Count Up to 9.4×109/L.
Bone marrow MICM typing (another hospital): morphology (M): 94.2% were lymphoblasts and prolymphocytes, large cell body, regular nuclei, less cytoplasm, stained blue, vacuoles in some cells. Flow immunophenotyping (I): 84.5% were abnormal B lymphoblasts, highly expressing CD19, CD22, CD38, HLA-DR, CD58 and cCD79a, partially expressing CD10, and not expressing cIgM. Cytogenetics (C): 46, XX, der(19)t(1;19)(1;19)(q22; p13) [10] Molecular biology (M): fusion gene screening: positive E2A-PBX1 fusion genes, not quantified. Mutations of hematological malignancy-associated genes were not examined.
(Primary disease) systemic extramedullary evaluation: cerebrospinal fluid cytofuge + flow immunophenotyping suggested the presence of leukemia cells.
Imaging Evaluation Was Not Performed.
Diagnosis And Differential Diagnosis
1. Extramedullary relapse of primary B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: When the child developed primary disease, the bone marrow chromosome had t (1; 19) (q22; p13), and although it was not the common t (1; 19) (q23; p13), the fusion gene screening found positive E2A-PBX1. The child was considered with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with positive E2A-PBX1. In children with such fusion genes, extramedullary leukemia is prone to occur during onset and treatment. At onset, the children have central nervous system leukemia and also meet the clinical features of such cases. Therefore, on admission, the right mandibular mass was highly suspected as extramedullary relapse of this disease, and E2A-PBX1 detection in the right mandibular mass should be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
2. Secondary lymphoma: E2A-PBX1 was positive in fusion gene screening at the initial onset of the disease, but it was not verified by FISH and fusion gene quantification. No E2A-PBX1 fusion gene quantification was monitored during the treatment, so it was not possible to evaluate when the patient achieved molecular remission. The right mandibular mass was only pathologically and immunohistochemically examined in the local hospital, and flow cytological detection was not performed to compare whether its immunophenotype was consistent with the immunophenotype of the bone marrow tumor cells at initial onset, so the possibility of secondary lymphoma could not be excluded.
Diagnosis Method:
No tumor cells were detected in the bone marrow and cerebrospinal fluid of the child on admission, so it was not possible to verify whether the diagnosis at the initial onset was correct. Therefore, the bone marrow smear and the pathological slide of the right mandibular mass of the child were taken for TCF3/PBX1 FISH test.
Results of the FISH test of bone marrow smear at initial onset (see Figure 1): In the 400 bone marrow cells analyzed, the number of cells fused detected at TCF3/PBX1 gene locus was 114 (28.5%), which was greater than the threshold for a positive result, suggesting the presence of E2A-PBX1 fusion genes. The child was confirmed with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with positive E2A-PBX1 fusion genes.
Results of the FISH test of pathological slide of the right mandibular tissue: In the 100 histocytes analyzed, the percentage of infusion cells was 34%, which was greater than the threshold for a positive result, suggesting the presence of E2A-PBX1 fusion genes. It was confirmed that E2A-PBX1 fusion genes were also present in the tumor cells in the right mandibular mass of the child, and the child was finally confirmed with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with positive E2A-PBX1 fusion genes and extramedullary relapse.
 Beijing Hightrust Diagnostic Co., Ltd.
Beijing Hightrust Diagnostic Co., Ltd.
No. 1, North Disheng Street, Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area
Building 3 and 4, 010-67871322
FISH test report
FISH-R001.05 (20170721)
| Name: | Gender: female | Age: 7 years old | Specimen No.: H18052515 | |||
| ID No.: | Specimen type: initial bone marrow slide | |||||
| Submitting hospital: Beijing Boren Hospital | Type of visit: others | |||||
| Admission No./Patient No.: 001713 | Department: Eighth ward | Bed No.: 13 | Submitting doctor: Zhuojun LING | |||
| Collection time: | Reception time: May 25, 2018 17:45:12 | Test barcode: 1527244109869311 | ||||
| Clinical diagnosis: relapsed B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma | ||||||
| Test Method: FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) | Testing instrument: fluorescence microscope (BX53) | |||||
Test Method:

Test Results:
Nuc ish 19p13.3 (TCF3х).1q23 (PBX1х2) (TCF3 com PBX1х1) [114/400]
In the 400 bone marrow cells analyzed, the number of cells fused detected at TCF3/PBX1 gene locus was 114 (28.50%), which was greater than the threshold for a positive result (9.12%). The above result suggests that the TCF3/PBX1 gene locus fusion is positive.
Please combine the other test results (such as: karyotype, flow cytometry or genetic testing) and clinical symptoms for comprehensive analysis.
Picture:

Report time: May 30, 2018 Reported by: Yujie ZHANG
Reviewed by:
Laboratory's statement: The result of the report is only responsible for the
tested specimen. Analysis of a limited number of cells cannot reveal all
possible clonal DNA abnormalities in the patient. Because the specimen can be
kept for a certain limited period, if there is any doubt about the result of the
report, please submit a re-test application within 15 days from the date of
issuance of this report, and an overdue will not be accepted.

Beijing Hightrust Diagnostic Co., Ltd.
No. 1, North Disheng Street, Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area
Building 3 and 4, 010-67871322
FISH test report
FISH-R002.05 (20170721)
| Name: | Gender: female | Age: 7 years old | Specimen No.: H18052106 | |||
| ID No.: | Specimen type: tissue for biopsy | |||||
| Submitting hospital: Beijing Boren Hospital | Type of visit: others | |||||
| Admission No./Patient No.: 001713 | Department: Eighth ward | Bed No.: 37 | Submitting doctor: Zhuojun LING | |||
| Collection time: May 17, 2018 | Reception time: May 21, 2018 18:12:48 | Test barcode: 152689715378211 | ||||
| Clinical diagnosis: relapsed B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma | ||||||
| Test Method: FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) | Testing instrument: fluorescence microscope (BX53) | |||||
Test Method:

Test Results:
In the 100 histocytes analyzed, the percentage of infusion cells was 34.00%, which was greater than the threshold for a positive result. The above result suggests that the TCF3/PBX1 gene fusion is positive. Please combine with other test indicators for comprehensive analysis.
Picture:
Report time: May 25, 2018 Reported by: Yujie ZHANG
Reviewed by:
Laboratory's statement: The result of the report is only responsible for the tested specimen. Analysis of a limited number of cells cannot reveal all possible clonal DNA abnormalities in the patient.

Figure 1. FISH Test of Bone Marrow Smear And Pathological Biopsy Tissue at Initial Onset
Treatment Process
After 1 year of treatment, PET-CT showed early extensive extramedullary relapse, suggesting poor prognosis. After admission, VLD (Dex 20 mg/m2 × 4 d + L-ASP 10,000 units × 4 d + VDS 1 mg d1) was given for re-induction, and the mass was shrunk transiently and then enlarged rapidly, so such patients had low complete remission rate and low long-term disease-free survival rate after chemotherapy. After communication with the family members, they agreed to enter the clinical trial on autologous murine CD19-CART therapy. The peripheral blood lymphocytes of the child were collected to culture murine CD19-CART cells.
Preparative regimen for CART from May 28, 2018 to June 4, 2018: VLD+IDA+Flud+CTX
June 6, 2018 (0d): back infusion of CD19-CART cells 4.28×106/kg.
June 10, 2018 (+4d): fever, rapidly enlarged right mandibular mass, high skin temperature, tenderness and rejection to touch.
June 12, 2018 (+6d): ALT/AST increased by 4 times, body flushing and edema. The right mandibular mass was progressively enlarged, involving the mandibular body and neck and compressing the trachea. Methylprednisolone 20 mg was given through a murphy's dropper to control CRS.
June 14, 2018 (+8d): heat was relieved, liver function returned to normal, systemic edema disappeared, right mandibular mass disappeared, and CRS was at grade 2 (see Figures 2-3).
July 9, 2018 (+33d): hemogram was recovered, bone marrow and cerebrospinal fluid evaluation: molecular remission status. Imaging evaluation PET-CT (see Figure 4): multiple hypermetabolic lesions disappeared.
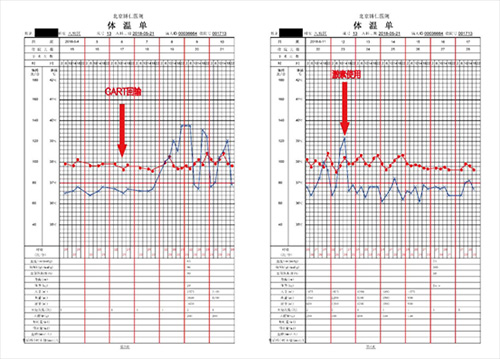
Figure 2. Changes in body temperature during treatment
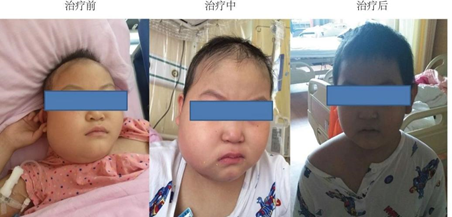
Figure 3. Comparison Before And After Treatment
+33d after treatment before treatment
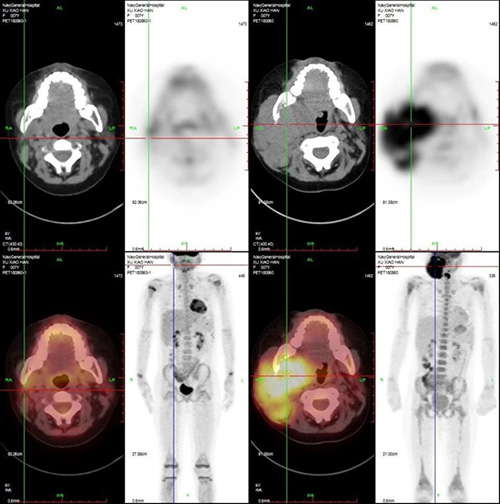
Figure 4. Imaging (PEC-CT) Before And After Treatment

Figure 5. Changes in The Proportion of CART Cells During Treatment
Subsequent Treatment Regimen:
The child underwent head + total spinal cord + right mandibular radiotherapy from July 13, 2018 to August 3, 2018, the family members refused to perform allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and the familial genetic susceptibility gene screening (see Figure 6) indicated no clearly pathogenic high-risk genes, so it was planned to perform sequential autologous humanized CD22-CART cell therapy in our hospital on August 10, 2018.
Figure 6. Screening of Familial Genetic Susceptibility Genes in Hematological Malignancies
Request an Appointment
Whether you are ready to make an appointment now or have questions for our expert team, we are standing by to help.
Email: international.service@gobroadhealthcare.com Phone: +86 010-83605002/010-83605200 Online Access









